Access point ‐ A term typically used to describe an electronic device that provides for wireless connectivity via a WAN to the Internet or a particular computer facility.
Duty cycle – A measure of the percentage or fraction of time that an RF device is in operation. A duty cycle of 100% corresponds to continuous operation (e.g., 24 hours/day). A duty cycle of 1% corresponds to a transmitter operating on average 1% of the time (e.g., 14.4 minutes/day).
Electromagnetic field (EMF) ‐ A composition of both an electric field and a magnetic field that are related in a fixed way that can convey electromagnetic energy. Antennas produce electromagnetic fields when they are used to transmit signals.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) ‐ The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the US Federal Government and is directly responsible to Congress. The FCC was established by the Communications Act of 1934 and is charged with regulating interstate and international communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable. The FCC also allocates bands of frequencies for non‐government communications services (the NTIA allocates government frequencies). The guidelines for human exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic fields as set by the FCC are contained in the Office of Engineering and Technology (OET) Bulletin 65, Edition 97‐01 (August 1997). Additional information is contained in OET Bulletin 65 Supplement A (radio and television broadcast stations), Supplement B (amateur radio stations), and Supplement C (mobile and portable devices).
Gigahertz (GHz) ‐ One billion Hertz, or one billion cycles per second, a measure of frequency.
Hertz ‐ The unit for expressing frequency, one Hertz (Hz) equals one cycle per second.
Megahertz (MHz) ‐ One million Hertz, or one million cycles per second, a unit for expressing frequency.
Mesh network ‐ A network providing a means for routing data, voice and instructions between nodes. A mesh network allows for continuous connections and reconfiguration around broken or blocked data paths by “hopping” from node to node until the destination is reached.
Milliwatt per square centimeter (mW/cm2) ‐ A measure of the power density flowing through an area of space, one thousandth (10‐3) of a watt passing through a square centimeter.
Microwatt per square centimeter (μW/cm2) ‐ A measure of the power density flowing through an area of space, one millionth (10‐6) of a watt passing through a square centimeter.
Radiofrequency (RF) ‐ The RF spectrum is formally defined in terms of frequency as extending from 0 to 3000 GHz, the frequency range of interest is 3 kHz to 300 GHz.
Repeater unit ‐ A device that can simultaneously receive a radio signal and retransmit the signal. Repeater units are used to extend the range of low power transmitters in a geographical area.
Router ‐ An electronic computer device that is used to route and forward information, typically between various computers within a local area network or between different local area networks.
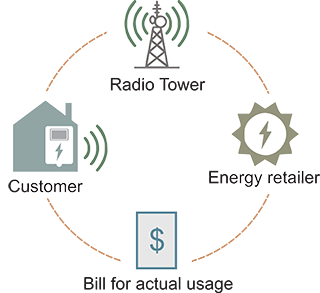
Advanced meter ‐ A digital device for measuring consumption, such as for electricity and natural gas, and sending the measurement to a utility company. Automated meter reading (AMR) meters send information one‐way only. Automated meter infrastructure. (AMI) meters are capable of two‐way communications. Specific absorption rate (SAR) ‐ The incremental energy absorbed by a mass of a given density. SAR is expressed in units of watts per kilogram (or milliwatts per gram, mW/g).
Transmitter ‐ An electronic device that produces RF energy that can be transmitted by an antenna. The transmitted energy is typically referred to a radio signal or RF field.
Wide area network (WAN) ‐ A computer network that covers a broad area such as a whole community, town, or city. Commonly, WANs are implemented via a wireless connection using radio signals. High‐speed Internet connections can be provided to customers by wireless WANs.
Wi‐Fi ‐ An name given to the wireless technology used in home networks, mobile phones, and other wireless electronic devices that employ the IEEE 802.11 technologies (a standard that defines specific characteristics of wireless local area networks).
- California Council on Science and Technology